Neural Networks are the most prominent area where Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are being used to revolutionize how people use Technology. This practical Guide will provide a clear explanation of Neural Networks, so that anyone interested in understanding the Basics and Applications can do so.
At its simplest level, Neural Networks are computer-based Systems designed to mimic the Human Brain. The Structure of these Systems consists of Layers of Interconnected Nodes (often referred to as “Neurons”) that Process Data by Recognizing Patterns within the Data. Similar to how the Human Brain Learns From Experience, Neural Networks Learn to complete tasks by adjusting the Connections Between the Neurons.
Summary
Artificial Neural Networks are models of learning based on the pattern-recognition capabilities of neural connections and layering. This overview will describe the layers (input, hidden, output) of artificial neural networks, the process of “back-propagation” to train an artificial neural network, some examples of where neural networks are applied in various industries, the advantages of using artificial neural networks (highly accurate models) and the challenges associated with the application of artificial neural networks (high computational requirements, and the potential for over-fitting). Additionally, this guide will help beginners get started with artificial neural networks by listing two shared neural network libraries (TensorFlow and PyTorch) and some online tutorial resources.
How Do Neural Networks Work?
The input layer of a neural network receives unprocessed data, the hidden layer(s) carry out operations that are more complex than simple arithmetic (and also perform pattern recognition), and the output layer displays the final result of this operation; i.e., in addition to classification of images, it can predict a number.
What are Neural Networks?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) rely heavily on Neural Networks, modeled after the way our brains process and evaluate information. A Neural Network is essentially a series of interconnected “layers” of “nodes,” or “neurons.” Each node uses a set of predefined mathematical formulas to transform the input data; the transformed data passes through multiple layers of nodes.
As data flows through the network, nodes learn to connect, enabling them to identify patterns in the training data and improve their ability to perform tasks. These characteristics have allowed Neural Networks to excel at a variety of applications, including image recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making.
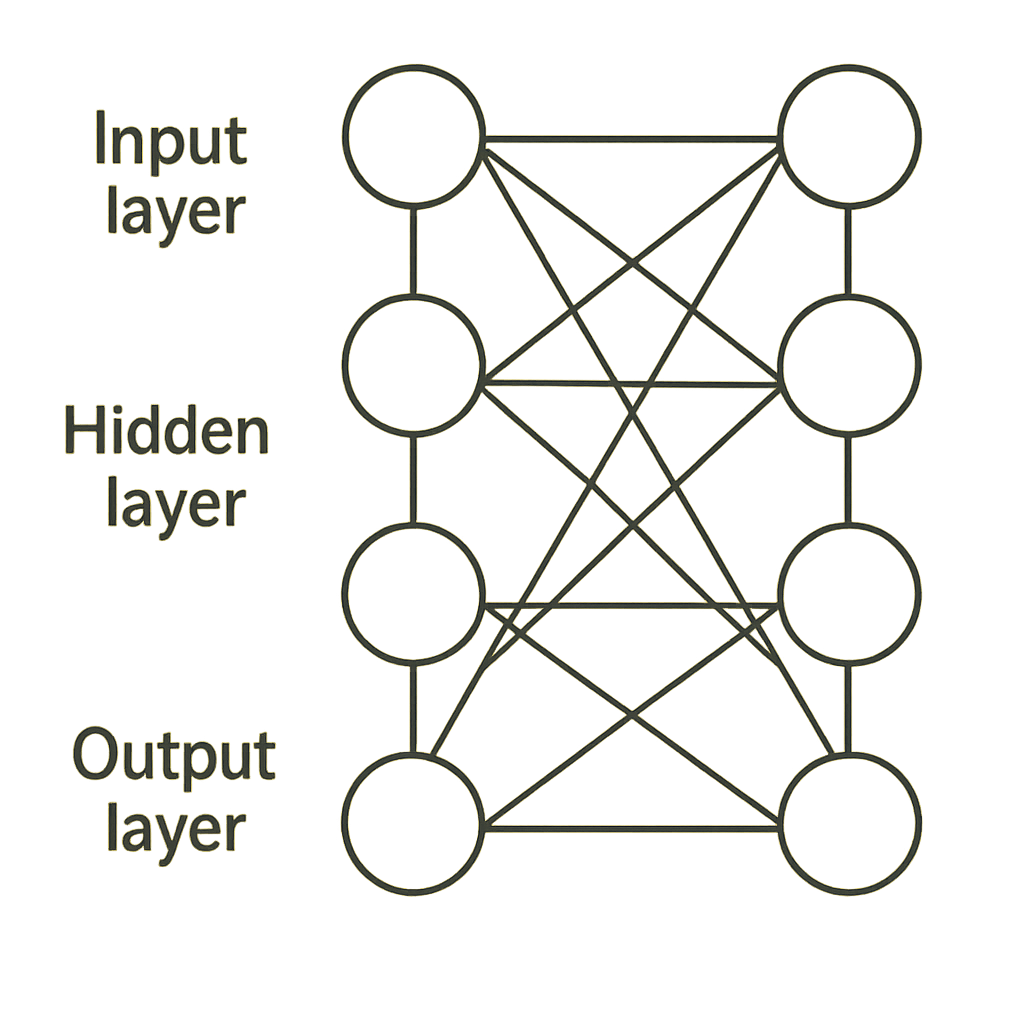
A standard Neural Network includes three primary layers: an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. The Input Layer accepts input data into the system; the Hidden Layers take the input data and perform calculations to derive useful features.
Finally, the Output Layer generates results, such as classifications and predictions, depending on what the network is performing. By applying large amounts of data to a network, it can learn to recognize a wide variety of complex patterns and generate accurate predictions, leading to significant breakthroughs across industries such as Healthcare, Finance, and Technology.
Importance in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are two of many disciplines focused on developing computer-based systems that can improve their performance over time through learning. The implications of these new technologies are numerous and will likely be felt across every aspect of society (e.g., healthcare, financial services, transportation). Thus, the importance of studying machine learning and artificial intelligence cannot be overstated.
Machine learning enables computers to identify patterns in vast amounts of data and use this information to generate predictions that aid decision-making and optimize processes across multiple industries. Therefore, as technological advancements continue to unfold, it is increasingly important for individuals and organizations to understand the value of machine learning and artificial intelligence so they can leverage these technologies to develop innovative products/services and maximize operational productivity.
Training Neural Networks
Incorporating training into the construction of a neural network is an essential part of its overall development. During this training phase, the network is fed large volumes of data, and then uses that data to adjust (modify) the connection strength between each neuron based on the amount of error found in the final output. This back-and-forth, iterative training process is repeated until the network’s output is correct with sufficient accuracy.
The Structure of Neural Networks
Layers of a Neural Network
Most neural networks consist of many interconnected layers. These layers all operate together to accept input data, process it through multiple levels of decision-making, and ultimately provide an output based on the input to the network. There are generally three categories of layers within a neural network: Input Layers, Hidden Layers, and Output Layers.
The Input Layer is where the Data Enters the Neural Network. This layer receives the Input Values, which can be numeric, image-based, or any other data required to process. It is essential because it allows the Network to Start Processing the Data.
Hidden Layers are the Layers Situated Between the Input and Output Layers; they process the Data Sent to them by the Input Layer. Depending upon how complex the Task is, the Number of Hidden Layers and the Number of Neurons per Hidden Layer may vary. These Hidden Layers allow the Network to Identify Patterns & Features within the Data to Predict Classifications Accurately.
Finally, the Output Layer Provides the Network’s Processing Results. The Output Layer Provides the Final Answer Based Upon the Computations Conducted in the Previous Layers. The Output May Take on Many Forms, i.e., Class Label Classification or Numerical Value Regression. All Three Layers Allow the Network to Learn from Data to Make Informed Decisions Based Upon That Learning.
Input Layer
The input layer acts as the gateway to the data fed into an artificial neural network and, therefore, as the first layer of processing in the network. Essentially, the input layer takes all the input data (e.g., images, text, numbers) that feed into the network, depending on what the neural network was designed to do.
Every neuron/node in the input layer relates to one of the attributes/features of the input data. This depends on the size/dimensions of the dataset the user inputs into the input layer. As such, when the neural network has properly organized the data at the input layer, it then proceeds to multiple layers of calculations and transformations that lead to a correct prediction or classification.
Hidden Layers
The hidden layers in Neural Networks allow the Network to preprocess data before producing the final output. Hidden layers are called “hidden” because their operations cannot be seen either at the input or the output level.
The hidden layers can determine complex relationships by having multiple layers of neurons that perform various types of mathematical operations, thereby allowing the network to learn more about complex concepts.
A typical Neural Network will have at least one, and possibly multiple, hidden layers. The more hidden layers that a model has, the greater its capacity is to understand the complex relationships within a dataset. For example, in Image Recognition, the first hidden layer typically identifies simple edge characteristics, and subsequent layers identify more complicated shapes, etc. It is vital how you define the number of hidden layers and how many neurons per layer,
since if there are too few layers, you will limit the amount of learning the model can do, but if there are too many layers (or too many neurons) you may create noise. Your model will become less effective on new data.
To conclude, Hidden Layers are an essential component of successful neural networks. When you stack layers of neurons deep enough, Deep Learning Models can identify sophisticated features in large datasets and therefore excel in applications such as natural language processing and image recognition. Improving how we design the hidden layer remains a key area of research for advancing Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Output Layer
The Output Layer represents the last layer of a neural network, and at this point, the results of all of the work done in previous layers have been processed into a form that can be used to complete the intended task(s).
This layer organizes the previously processed and transformed information from prior layers into an understandable format that can be used for a variety of applications (e.g., classification, prediction). Typically, the Output Layer includes one or more neurons that represent the neural network’s “desired” output (i.e., the classification result, predicted value, etc.).
Additionally, the Output Layer often uses activation functions suited to the task at hand. An example of this would be applying a Softmax activation function during a classification task to ensure the resulting probability values sum to 1 (i.e., reflect the probability of each possible class) and applying a linear activation function during a regression task to produce continuous numerical predictions. As such, the Output Layer is a vital part of the neural network’s overall structure, as it provides the network’s final output.
How Neurons Interconnect and Process Data
Neurons are specialized cells in the brain and nervous system that play a crucial role in processing and transmitting information. These cells communicate with each other through synapses, tiny gaps between the ends of one neuron and the beginning of another. When a neuron receives a signal, it can generate an electrical impulse that travels down its axon, reaching the synapse.
At this point, neurotransmitters are released, crossing the synapse to bind with receptors on the receiving neuron. This process enables the transmission of information across vast networks, where complex connections allow data to be processed.
The way neurons are interconnected is essential for understanding how information is processed in the brain. Each neuron can connect with thousands of other neurons, forming intricate networks that support various functions, such as sensations, thoughts, and movements. The strength and efficiency of these connections can change over time, a process known as synaptic plasticity.
This adaptability is fundamental to learning and memory, as it allows neural pathways to be strengthened or weakened by experience. Overall, the interconnectivity of neurons is central to the brain’s ability to process information and respond to the environment effectively.
The Learning Process
Understanding Training and Backpropagation
Training machine learning models is a fundamental process in which the model’s parameters are adjusted to produce accurate predictions. Training occurs by presenting the model with a large amount of labeled data, including both input and the correct output associated with that input.
During training, the model will continually learn from patterns in the provided data and adjust its parameters to minimize error. Back propagation is used during the training process, where gradients are calculated to indicate how much the output changes with changes in the model’s parameters.
There are two phases in backpropagation: the forward pass and the backward pass. During the forward pass, the network takes input data and produces an output, which is then compared to the actual (or true) label using a loss function. Following the comparison of the predicted output versus the actual output using a loss function, the backward pass uses the chain rule of calculus to calculate the gradients of the loss with respect to each parameter of the model.
Using these gradients, the model can update its parameters via an optimization algorithm, such as stochastic gradient descent, to minimize the loss. This cycle of parameter updates to minimize loss continues across multiple cycles, also called epochs, until the model reaches an acceptable level of accuracy.
The Role of Data in Training Neural Networks
- Training Neural Networks depends heavily upon data.
- Neural networks process an enormous amount of data to “learn”.
- The data can be in a variety of formats (images, text, numbers).
- High-quality data will improve the prediction/classification accuracy of your models.
- The Data is split into three primary categories during training:
- The Training Set: Teaches the Network.
- The Validation Set: Assesses the Model’s Performance during Training.
- The Testing Set: Evaluates the Model’s Performance using Unseen Data after training.
- Selecting/Preparing these Datasets Properly is very Important.
- The Quality and Quantity of the Data are critical to train a Neural Network successfully.
Real-World Applications of Neural Networks
One of the advantages of neural networks is their versatility and use in many different areas of study. Following is an example of this:
- Speech and Image recognition: Since neural networks can identify patterns, they are excellent at recognizing images and speech.
- Natural Language processing (NLP): They are being used in chatbots and translation software to both recognize and generate human language.
- Medical/Health Care: Neural Networks are assisting doctors with disease diagnosis through the analysis of medical images, as well as with the prediction of patient outcomes.
- Stock Market/Fraud Detection: They are helping to predict stock market trends and detect fraud from financial transactions.
Image and Speech Recognition
image and speech recognition; image (or object) recognition; speech or voice recognition. These are sophisticated technologies that allow computers to read visual information and interpret human speech. The goal of image recognition is to analyze an image and identify objects, scenes, and other elements within it. It employs many different methods and techniques to enable computers to perceive, much like humans do visually.
Speech recognition, on the other hand, converts spoken language to written text by using speech (voice) and interpreting audio signals to identify words/phrases, ultimately enabling computers to understand and react to user verbal input. There are numerous uses for both technologies such as enhanced user experience through mobile devices/virtual assistant technology and greater accessibility for people with disabilities. As both areas continue to evolve, they will provide better accuracy, efficiency, and the ability to adapt to a variety of languages/dialects.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP (Natural Language Processing) is a fascinating subfield of computer science & AI that focuses on the interface between computers and humans using natural language. The overall goal of NLP is to enable computers to understand & interpret human language & generate responses that are both meaningful & valuable.
Some of the many NLP-related activities & challenges include: interpreting text, responding to users conversationally, determining the positive/negative sentiment in communications, and more. Due to its capabilities, NLP has been applied across a variety of domains (customer support, language translation, etc.) for data analysis.
The processes & methodologies associated with NLP utilize sophisticated algorithms & models to analyze linguistic characteristics (grammar, syntax, semantics). Researchers & developers have been using Machine Learning (ML), a technique that allows computers to “learn” from massive amounts of data, to achieve this task. ML enables computers to refine their ability to comprehend and generate human language continually.
Some examples of how NLP is being applied include voice-controlled personal assistants, chatbots & automated translation tools, all of which help create fluid interactions between humans and technology. In summary, NLP will continue to be a significant aspect of the growth & development of Intelligent Systems designed to enhance human-computer interfaces.
Healthcare Applications
Applications in healthcare have significantly impacted how doctors and other medical professionals care for their patients. They make many everyday tasks easier, which in turn allows professionals to provide higher-quality service.
Healthcare applications vary from simple mobile applications that monitor an individual’s health status to very complex applications that help manage an individual’s patient record and appointments. The way applications are used has led to significant changes in the interaction between patients and their providers, as well as positive impacts on patients’ health outcomes.
In addition to changing the interaction between patients and their providers, healthcare applications have also enhanced healthcare providers’ ability to communicate with each other and with their patients. These applications provide a secure way to message, schedule appointments, and share medical information in real time.
The rapid exchange of this information is one of the factors that can lead to a quicker diagnosis and a better plan of action for treating a patient’s condition. Furthermore, healthcare applications provide patients with access to educational materials, personal health advice, and reminder functions that promote proactive health management.
The increased use of data analysis in healthcare applications has enabled healthcare providers to collect and analyze large amounts of health-related data. This provides healthcare providers with the opportunity to identify trends in health conditions, enhance protocols for providing healthcare to individuals, and support preventive measures.
Therefore, through the use of technology in healthcare applications, the specific needs of each patient are being met while improving the entire healthcare system. These types of applications will likely become even more critical for the efficient and effective delivery of patient-centered care as the healthcare industry continues to evolve.
Financial Sector Applications
Technology has transformed the way banks and other financial institutions operate and serve customers, enabling greater transactional efficiency, improved risk assessment, and enhanced customer service.
The technological advancements in the financial services industry, such as mobile banking apps that will allow consumers to conduct banking activities on their mobile devices, demonstrate how technology can improve business performance and create new ways to serve individuals. There is also increasing use of complex computer algorithms to perform tasks such as analyzing market trends to identify potential investment opportunities.
As a result, there is a need to continue reviewing and assessing the impact of these technologies on both individual consumers and business operations to understand the implications of their adoption
Advantages of Neural Networks
High Accuracy in Predictions
High-accuracy predictions occur when a prediction tool or method produces a forecast that closely matches actual results. High accuracy can be achieved by using advanced mathematical formulas (algorithms) and large amounts of data to analyze patterns and trends that exist within the data.
As a result of the accuracy provided by these prediction tools, users have greater confidence in their forecasts, as they can depend on them to help make informed choices across all areas, including but not limited to financial, health care, and weather. Users need to have faith in their prediction tool(s), as accurate predictions can help make better plans, allocate resources, and ultimately achieve better outcomes, both personally and professionally.
Learning from Large Data Sets
Organizations have become increasingly reliant on analysis of large datasets in this age of data science and analytics. The more an organization collects about its customers, operations, and/or performance, the greater the need to develop effective means to analyze the information.
In addition to using numerous techniques to analyze extensive data collections (e.g., identifying trends and patterns), the results of these analyses enable organizations to make better decisions and enhance operational efficiency across industries such as finance, healthcare, and marketing.
Analyzing large datasets requires more than simply possessing the appropriate methods and algorithms. Analyzing large datasets requires more sophisticated machine learning processes that allow computers to independently discover patterns in data and create forecasts based upon those discoveries with minimal human intervention.
Organizations that have successfully applied predictive analytics have enhanced their customer service and products by leveraging machine learning capabilities. Organizations that use Big Data technologies, such as Hadoop and Spark, can also efficiently process, and store massive amounts of data.
While there are many benefits to analyzing extensive data collections, the challenges involved should not be ignored. One of the most significant challenges when processing extensive data collections is ensuring the accuracy of the data being analyzed. If the data analyzed is incomplete or inaccurate, the analysis may not accurately reflect the organization’s data.
Another challenge associated with processing extensive data collections concerns privacy and ethical issues. For example, organizations operating in the finance or healthcare industries often possess personal identifiable information (PII) that must be protected. Ensuring proper data governance and regulatory compliance can help organizations mitigate risks associated with processing large datasets while providing valuable insights into their business.
Overall, analyzing extensive data collections can provide organizations with significant opportunities for growth and improvement. Organizations can capitalize on the advantages of extensive data collections by developing and implementing advanced analytical methods and techniques, investing in the necessary IT infrastructure to support analysis, and developing strategies to address data quality and privacy challenges.
As organizations continue to collect larger volumes of data, the ability to analyze and leverage the knowledge contained in these collections will become critical to their success.
Challenges and Limitations
Computational Requirements
Assessing the computational needs of an application or system involves evaluating the hardware and software components needed to support its efficient operation. The most common examples of this are CPU and RAM, as well as storage requirements. Operating systems also need to be compatible with an application or system to operate at optimal levels.
Understanding the hardware and software requirements for an application or system ensures the end-user can use it without experiencing performance issues or malfunctions. A complete analysis of the hardware and software requirements for using an application or system will provide the best possible user experience.
Overfitting and Its Implications
- When a model fits the training data too closely, it picks up all the variations and noise in the data; this is called overfitting.
- A model can do very well with the training data, yet fail miserably with new, unseen data.
- In many real-world situations, the data being used will vary significantly from what was used to train the model resulting in some poor decisions based on an inaccurate prediction.
- It is essential to address the issue of overfitting when building effective predictive models.
- Overfitting can have serious consequences in areas such as financial forecasting, medical diagnosis, and marketing.
- Using overfitting models can cause poor decision-making by creating inaccurate predictions, such as recommending bad investments or misdiagnosing medical conditions.
- Methods to help eliminate overfitting include cross-validation, regularization, and the use of a less complex model.
- Helping to develop predictive models that can both accurately fit the training data and work reliably in real world applications is achieved through addressing overfitting.
Getting Started with Neural Networks
Recommended Tools and Frameworks
When choosing tools and frameworks for software development, it’s essential to explore options that can enhance productivity and improve the final product.
Different tools assist with various development aspects, such as programming languages, libraries, and environments. Frameworks offer pre-built components and best practices, simplifying the process. Evaluating these tools closely can speed up development and strengthen collaboration.
It’s also essential to assess project needs when selecting tools and frameworks. Consider the project’s goals, the team’s skills, and existing technologies.
By understanding these factors, developers can choose tools that align with their objectives and enhance their work. Staying up to date on new tools and frameworks is vital as technology evolves rapidly. New solutions can provide improved features and efficiency, offering significant advantages for projects.
Ultimately, making informed choices about tools and frameworks leads to a better development experience. These decisions can boost collaboration, efficiency, and adaptability to changes. Therefore, thorough research and careful consideration of all options are crucial.
Conclusion: The Future of Neural Networks in Technological Advancements
Neural Networks hold great promise for advancing multiple technologies in the years ahead. We should expect that as time passes, the models will become increasingly advanced and sophisticated. Neural Networks can positively impact a wide range of disciplines, including Artificial Intelligence, Healthcare, Finance, and many others. The more we advance the field of neural networks, the more innovative applications we should be able to develop that will positively affect industry and our day-to-day lives. The integration of neural networks into systems will probably result in better efficiencies, increased accuracy, and transformational solutions to a multitude of issues.