Have you ever spent hours reading multiple hundred hotel reviews to see which hotel was really great? On top of the fact that there are some hotels that rave about the “great staff,” while others have a totally opposite review, saying the hotel is a “total disaster.”
Examining all the opinions on hotels can be exhausting. What if a computer could take seconds to read every single comment about your hotel stay and then give you an idea of the overall feel of those comments? That’s essentially what the concept of Sentiment Analysis does.
Sentiment Analysis, or Artificial Intelligence, works quietly in the background throughout the internet. This is why a company will immediately recognize when a customer (voice of the customer) is unhappy with their service and tweets about it. Additionally, a movie website can provide a summary of what thousands of viewers thought about a movie.
Sentiment Analysis has also been referred to as “Opinion Mining. The primary function of Opinion Mining is to read a piece of text and then classify the emotion behind it as Positive, Negative, or Neutral.
Have you ever spent hours reading multiple hundred hotel reviews to see which hotel was really great? On top of the fact that there are some hotels that rave about the “great staff,” while others have a totally opposite review, saying the hotel is a “total disaster.”
Examining all the opinions on hotels can be exhausting. What if a computer could take seconds to read every single comment about your hotel stay and then give you an idea of the overall feel of those comments? That’s essentially what the concept of Sentiment Analysis does.
Sentiment Analysis, or Artificial Intelligence, works quietly in the background throughout the internet. This is why a company will immediately recognize when a customer is unhappy with their service and tweets about it.
Additionally, a movie website can provide a summary of what thousands of viewers thought about a movie. Sentiment Analysis has also been referred to as “Opinion Mining. The primary function of Opinion Mining is to read a piece of text and then classify the emotion behind it as Positive, Negative, or Neutral.
What Is Sentiment Analysis, Really? The Three-Pile Sorting Method
At its heart, sentiment analysis is nothing more than a high-speed way of sorting people’s opinions by emotion.
If you had a huge stack of customer comments from cards or pieces of paper and your task was to separate them into two piles (one with good things to say about something, and one with bad things to say) and a third for just facts, then the computer would be doing the same thing, but with millions of tweets, review posts, and e-mail messages instantly. This is how customer sentiment is monitored in bulk.
The learning machine classifies comments into three primary types of “polarity analysis” of “text”.
Positive: The Comment is Positive; The Comment Expresses Satisfaction, or Happiness. (example: “The Camera on this Phone is Incredible.”)
Negative: The Comment is Negative; The Comment Expresses Anger, Frustration, or Disappointment. (example: “My Package Arrived Broken.”)
Neutral: The Comment is Neutral; The Comment is A Factual Statement or a Direct Question, No Strong Emotion. (example: “The Headphones Are Available in Black or White.”)
Separating Neutral Comments Is Key to Real-Time Sentiment Analysis. Sentiment Analysis Isn’t Just Finding Joy or Anger. It Is Also Knowing When a Comment Is Only Stating a Fact. This Technology Provides Businesses with a Powerful, Real-Time Snapshot of Public Opinion. And That Snapshot Allows Businesses to Improve Everything from Their Products to Their Customer Support.

Why Do Companies Care? From Faster Support to Better Products
Knowing there are 10,000 dissatisfied customers is one way to know this; however, it’s when we understand what they’re dissatisfied about and who needs our support first that the real power emerges. Companies can take an unending stream of customer feedback and transform it into actionable improvement plans based on its emotional content.
The company will implement two important changes that directly affect you, as a customer, to address issues you may have experienced in the past.
Companies that have the ability to understand and prioritize customer feedback will create tangible improvements that you have probably already noticed.
Get Help Right Away When Things Go Wrong
This tool works like an emergency room for customer service issues. When customers use language that indicates something is wrong (e.g., “my flight was cancelled,” or “your site isn’t working”) as opposed to a neutral complaint (“I wish I had more snack options”), those comments are highlighted so that a representative can quickly respond.
The bottom line is that you will receive assistance sooner rather than later.
Build What Customers Want
An application of this technology serves as a large, self-organised suggestion box. For example, if an app developer notices that many users are complimenting their app about a “new photo filter” but complaining about the “app draining my battery, the app developers now have a very clear understanding of which features to continue building upon and which are being built upon correctly.
This is not simply about determining what is good versus bad. It’s about leveraging the ability to listen to consumers in an unprecedented way by tapping the ever-growing, real-time stream of comments on social media and in online reviews. Continuous listening, as companies monitor brands, is known as brand monitoring and allows them to stay connected to the internet.
How Companies “Listen” to the Internet: The World of Brand Monitoring
Real-time is what Brand Monitoring is all about. Brand monitoring comprises multiple elements, but real-time listening is the primary one. That means that instead of waiting for customers to call you when they have a problem, Brand Monitoring systems can continually search the web for mentions of your company name, your product names, and people who represent your brand (like CEO’s).
A large element of this is Social Media Listening. Let’s say a new sneaker hits the market. Your tools will monitor comments on your Instagram account and analyze millions of public posts on social media sites such as Twitter and TikTok, as well as blog posts, for the name of your sneaker.
This will allow you to create a live dashboard to show how your customers are feeling – whether it is positive (excitement) or negative (disappointment). Using Text Analytics, you can quickly determine your customers’ feelings and categorize them into three categories: Positive, Negative, and Neutral.
Companies can be so responsive because of this immediate feedback loop. If there is a YouTube reviewer who just gave your company an extremely positive review, you can quickly see a positive wave coming from that influencer and then jump into promoting that positive review.
On the other hand, if a new software release causes people’s phones to crash and they begin posting about their anger with the app, the computer will detect a huge spike in negative posts and alert the engineers to a problem before it becomes national news. How would a machine know whether someone was excited or frustrated when reading a tweet? The answer is through the training process.
So, How Does a Computer Learn to Feel? A Tale of Two Methods
How can a computer tell that a tweet about your product or service was written because the user loved it, versus because they hated it? The first method was basically to create a high-tech version of Word Scramble. An algorithm (a computer’s instruction manual) was created using two dictionaries: a positive dictionary that included words such as “love,” “excellent,” and “perfect.”
There were also two negative dictionaries that contained words including “terrible,” “broken,” and “slow. When the computer scanned a sentence, it added points for positive words and subtracted points for negative words. And then declared what was best.
It is easy to see why using this simple process can lead to errors. For example, if a customer tweets “This was not the amazing experience I was hoping for, a simple point system may simply find the word “amazing” and place the comment in the “happy” category. I have read the words but totally missed their meanings. Therefore, using these simple systems to measure customer sentiment can yield inaccurate readings.
The approach to resolving this problem changed dramatically as an innovative strategy emerged: training computers using examples. Rather than providing word lists, programmers give the systems hundreds of thousands of real reviews written by people and labeled in advance.
A review will appear like “I love this product!” and be labeled “positive.” Another review would be shown, “Fell apart within a day,” and labeled “negative.” The computer would then analyze all those examples and develop its own understanding of how to recognize language patterns.
The above method is a simplified version of concepts from Artificial Intelligence. As an added benefit of this method, the computer begins to understand the context of what was being said; for instance, it recognizes that “not amazing” is the opposite of “amazing. Although this new method offers significant benefits, human communication can easily confuse the computer, and sarcasm is among the most difficult.
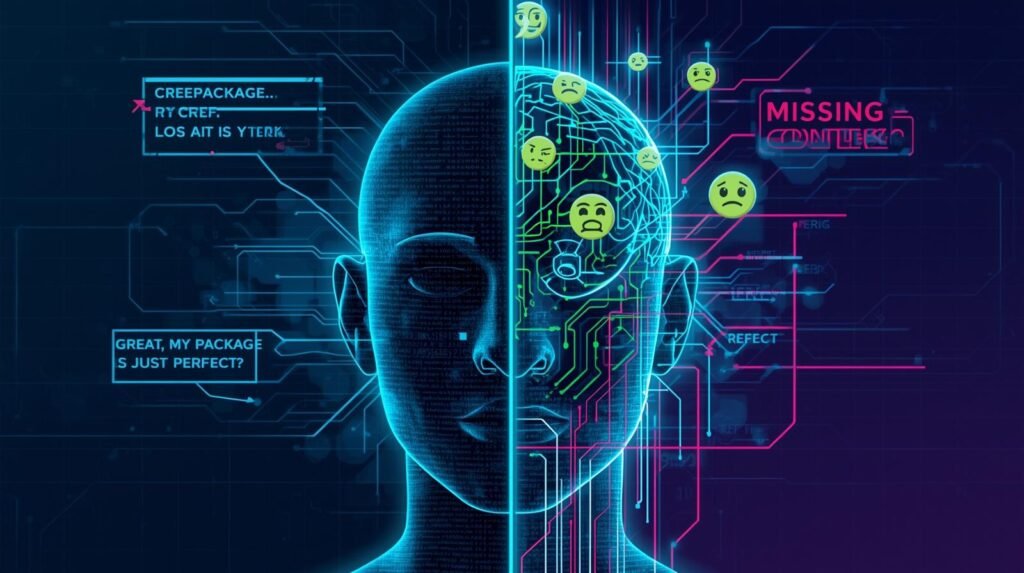
“Great, My Package is Lost. Just Perfect.” Why Sarcasm Is So Tricky
The phrase “Great, my package is lost. Just perfect” conveys an immediate emotional signal to humans. To computers, though, they’re likely to be confusing. A computer will see the positive keywords in the phrase (“Great”, “perfect”) and probably assign this comment a positive sentiment or happy tone — completely missing the anger expressed through the comment.
That’s why the difference between the literal language used and the intent of the message — which is common in all forms of sarcasm — creates such a challenge for computers trying to analyze the sentiment of comments.
The final piece of the puzzle for understanding A.I. is context. Context is the additional (surrounding) information that adds meaning to what you say.
Most humans can tell that “great” is used sarcastically when the entire sentence is “My package is lost.” Unfortunately, the A.I. is unable to link these ideas together with the same ease. The challenge in developing an application to analyze text polarity is the complexity of creating an A.I. that can interpret and follow the many unwritten rules we use to communicate through language.
Currently, determining whether a statement in text is sarcasm is a major area of study for researchers developing emotion-based A.I. applications. The technology is advancing rapidly, but it still has room for improvement. Even if a comment is obviously negative, there are other ways to find value. For example, knowing a customer is unhappy is different than knowing why they are unhappy.

Beyond ‘Good’ or ‘Bad’: Finding Out What People Like
While recognizing a review as negative is a positive step toward understanding customer comments about your company, it does not provide all of the information you will want to know. Take the example of a restaurant that receives an online review that states, “The pizza was delicious; however, the service was very slow.”
A negative rating for this review would give the owner no indication of problems with the food, personnel, pricing, etc., so the owner could make changes. To receive helpful customer feedback and understand what needs to change, organizations need to look beyond simple thumbs-up/thumbs-down ratings in reviews.
At this point, a more complex type of sentiment analysis comes into play. Sentiment analysis technology may identify the topic(s) (features/aspects) discussed by reviewers, rather than simply providing a thumbs-up or thumbs-down rating. The technology can assess the sentiment of each feature or topic individually.
Aspect-based Opinion Mining is similar to providing a product with a report card that shows how it performed across different criteria, rather than a simple letter grade.
At the detailed level for a business, this information will be highly valuable. The level of detail will enable the company to determine precisely what works and what doesn’t. For example,if we were analyzing a complex product (a new smartphone) and there were thousands of reviews, the company could use its analysis to provide a summary of all of these reviews at one time, such as this:
Camera: Good (“The photos are amazing”)
Battery Life: Bad (“Barely lasts a full day”)
Screen: Good (“The display is bright and clear”)
Price: Middle Ground (“It is priced similarly to other smartphones”)
This now gives the company a specific course of action: a robust marketing campaign to promote the camera’s excellent image quality and a specific area to focus on improving battery life. The company’s ability to receive specific, relevant, and timely feedback is greatly enhanced when it has a clear understanding of the customer’s needs and preferences, derived from analyses of these areas. However, just knowing that something is “good” or “bad” is only part of the emotional picture.
From ‘Happy’ to ‘Excited’: The Next Frontier of Emotion Artificial Intelligence
A review being “positive” tells you something, but it does not tell you everything about how the customer felt. There are many degrees of satisfaction; e.g., the customer may have been quietly satisfied with their purchase or very excited about it.
In addition to determining whether the review was overall positive or negative, emotion Artificial Intelligence (Emotion AI) can be used to identify the emotions the reviewer expresses—such as joy, anger, sadness, or surprise. The transition from positive/negative classification to emotion classification is analogous to the transition from a black-and-white photograph to a color photograph.
The potential for identifying subtle emotions is huge, particularly in customer support services. Consider a customer messaging about a defective product, and the system has identified basic dissatisfaction.
The automated response could include a return link to assist the customer. However, if the system identifies extreme anger or frustration, it can rapidly alert the message for a human agent to address as a priority. This emotionally intelligent Artificial Intelligence solution enables businesses to tailor their responses to customers’ true emotional states, resulting in faster, more effective resolutions.
By combining the “what” (e.g., battery performance) with the “how” (e.g., emotions such as frustration), this advanced NLP technology for emotion detection provides companies with a more detailed and accurate view of how customers feel about a product or service. Not only does it identify which issues need to be solved, but it also identifies which ones cause the greatest emotional distress to their users.
While this concept is becoming a reality through emerging technologies, many sophisticated tools are currently available that enable businesses to develop this type of detailed emotional intelligence.
The Toolbox: What Software Makes This All Possible?
In your mind, you could picture an engineering team working on developing such a system. In practice, most companies use prebuilt Voice of Customer platforms to develop their own emotion analysis systems. As such, a company need not be a major player in the technology field to understand what consumers say about it online. All they need is the right platform or tool.
These platforms can be viewed as a single, centralized hub for a company’s reputation. Rather than having someone manually search through tens of thousands of customer reviews, the Voice of Customer software will pull all relevant data from social media, support emails, and review websites. The Voice of Customer software will then run automated sentiment and emotion analyses on the collected data and display the results in charts, enabling managers to quickly identify trends and patterns in customer feedback.
The availability of this technology has made it affordable for businesses of every size to be able to perform powerful text analysis for brand tracking in “real time” as they listen to how consumers feel about their brands. The sheer number of organizations that have purchased these solutions makes them ubiquitous. So much so that companies use text analysis as a tool behind the scenes to influence and shape your buying decisions and what advertising you see.
How This “Invisible” Tech Shapes Your World
The customer’s opinions expressed through social media comments and reviews are being analyzed by sentiment analysis to provide insight into their views. As you take a second look at an item description or the stars assigned to it, you will now realize there is much more to that single digit than you once knew – there is a vast amount of data from hundreds/thousands of customers that has been translated into one numerical representation, thanks to sentiment analysis.
In addition to understanding this, you should also be aware of how much value your own input (a bad tweet or a great review) has today. This is because companies have begun using sentiment analysis to enhance customer experiences and respond to customer feedback on social media, enabling them to support customers more quickly and implement product changes. Your voice to a company can now get a response quicker than ever before.
The initial path to this new consciousness can be as easy as that: Notice. Each time you browse reviews on apps or watch a company respond immediately online, pause for a moment. The text classification is happening before your eyes, and with each instance, you’ll gain a deeper understanding. More than mere trivia, this information is Digital Literacy.
Understanding the fundamentals of sentiment analysis reveals one of the most important aspects of modern society. No longer are you a passive user; you are now a conscious Digital Citizen, with a clearer view of how your thoughts contribute to shaping the world of the internet that you use daily.
Q & A
- What is sentiment analysis (in simple terms)?
Sentiment analysis is a method that reads text (such as reviews, tweets, or support messages) and labels the sentiment behind it—usually positive, negative, or neutral. It doesn’t “feel” emotions the way people do. Instead, it looks for patterns in words and phrases that often match certain opinions. The main benefit is speed: it can scan thousands of messages and summarize the overall mood in minutes. - How does Artificial Intelligence figure out if a message is positive, negative, or neutral?
Most modern systems use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to prepare text (split it into parts, clean it, and turn words into numbers). Then, a trained model predicts the likely sentiment based on examples it has learned from previously. If it has seen many phrases like “works great” labeled positive and “stopped working” labeled negative, it learns those patterns. Some systems return a label, while others return a score (e.g., -1 to +1) along with a confidence level. - What’s the difference between rule-based and machine-learning approaches?
A rule-based approach uses predefined word lists and rules (for example, “love” = positive, “terrible” = negative). It’s easy to understand but often fails with context, negations (“not good”), and sarcasm.
A machine-learning approach learns from labeled examples and can handle greater natural-language variation. It’s usually more accurate in real-world writing, but it depends heavily on the quality of the training data and can still make mistakes when language gets tricky. - Why is sarcasm so hard for sentiment analysis?
Sarcasm often uses positive words to express a negative feeling (example: “Great, my package is lost.”). A system may see “Great” and guess “positive” unless it understands the full context. Humans use shared knowledge and tone cues that aren’t always present in plain text. Even advanced models can struggle when the “true meaning” contradicts the literal words. - Can sentiment analysis detect specific emotions, such as anger or joy?
Sometimes. Basic systems focus on polarity (positive/negative/neutral). More advanced emotion detection tries to label feelings such as joy, anger, sadness, or fear. This is more difficult because emotions overlap, people express them differently, and context matters substantially. Emotion labels also depend on the dataset used for training—if the training examples are limited, the emotion predictions can be unreliable. - What are the most common real-world uses—and what are the limits? Common uses include tracking customer feedback, monitoring social media reactions, triaging support tickets, and summarizing opinions about products or events through text analysis. The limits are important: models can be biased by their training data, misunderstand slang or sarcasm, and oversimplify mixed opinions (like “great camera, awful battery”). The safest approach is to treat results as signals, not facts—especially for sensitive decisions—and combine automated results with human review when stakes are high.