Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI). ML enables computers to learn from their experiences rather than receiving explicit programming instructions from humans. In essence, ML uses algorithms to identify patterns in large datasets and then uses those patterns to make informed predictions for new datasets.
Machine learning’s ability to accommodate a wide range of problems and domains, along with the types of data encountered, demonstrates a high level of flexibility. The versatility of machine learning and its importance to AI enable ML to play a critical role in AI’s continuous development. Additionally, the technology itself continues to evolve. Therefore, we can conclude that machine learning has become a crucial part of the AI ecosystem.
There are several machine learning techniques, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. These machine learning techniques employ distinct methodologies for developing and training models, giving researchers and practitioners the option to choose the approach based on the problem they aim to solve.
Machine learning algorithms can adapt and improve their efficiency and effectiveness over time by being trained on additional data. It is this ability to develop/adapt over time (learn) and continuously improve that makes machine learning applicable and successful across many industry applications, including financial services, where machine learning may assist with risk assessments, and healthcare, where machine learning can assist in disease diagnosis and tailoring patient care treatments
Summary
Machine learning (ML) is a much broader AI method that can learn to identify patterns in data through three different techniques – Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning – whereas Deep Learning (DL), is a specific subset of Machine Learning that uses a type of multi-layered neural network called an artificial neural network to automatically learn or find relevant features within large and complex datasets.
A few essential key differences exist between Machine Learning and Deep Learning, including the amount of data required to train models, the type of hardware needed, the amount of pre-processing or feature engineering that must be done before teaching a model, and the length of time it takes to train a model as well as the length of time it takes to infer results from a trained model.
Specifically, Machine Learning can operate effectively with small amounts of data, leverage expert-crafted features with modest hardware resources, and achieve faster training and inference times than Deep Learning. Conversely, Deep Learning requires a lot of data, can require the utilization of Graphical Processing Units (GPUs), can trade longer training times for faster inference times, and generally performs better with unstructured data such as images, speech, natural language processing, and other high complexity tasks for which automatic feature learning is beneficial.
As such, choose Machine Learning when you need a cost-effective solution that provides interpretability and is guided by your domain knowledge; select Deep Learning when you have a task that is one of vision, speech, natural language processing, or another high complexity task for which you want to take advantage of the ability to automatically learn features. Both Machine Learning and Deep Learning are used to build a wide range of applications across industries, including finance, health care, marketing, autonomous systems, and natural language technologies.

Supervised learning is one of the most common methods of machine learning. During supervised learning, an algorithm learns from labeled data. The dataset used during the supervised learning phase comprises the input features the model uses to generate outputs, along with the corresponding labels.
This allows the model to learn to map input data to their respective output values during supervised learning. Once the supervised learning phase is complete, the model can use what it has learned to predict outcomes for new input data it has not previously seen.
This type of learning is called example-based learning, as the model continually refines its predictive capabilities by adjusting its parameters to reduce error and improve accuracy. As a direct result of the refinement process, the model becomes increasingly capable of making more reliable and accurate predictions on future input data.
Supervised Learning is among the most widely used Machine Learning methods across numerous applications. It has been applied to spam filtering, where emails are categorized into two groups: spam and non-spam. Spam filtering enables users to filter their email inboxes and avoid unwanted messages. Supervised learning can also be used to classify images by identifying and labeling the object(s) contained in an image. An example would be classifying a photograph of a cat or a dog. A supervised learning model could determine whether the object shown in an image is a cat or a dog.
Supervised learning models are particularly effective at using prior experience to make reasonable predictions about new data they’ve never seen before; they do so by generalizing from previous experience. In addition to its ability to generalize, supervised learning is widely used in predictive analytics, which is employed extensively across businesses to predict future trends and events based on historical data.
Predictive capabilities such as these can be highly beneficial to businesses across many fields, including financial services and marketing, and help companies make decisions and develop long-term plans.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a branch of machine learning. It employs neural networks with at least three layers. They attempt to model how the human brain works so they can “learn” from large volumes of data. In contrast, many other machine learning models require features to be extracted manually from data, whereas others can automatically extract them and recognize complex relationships in the data.
Because they can operate at multiple levels of abstraction and are hierarchical, Deep Learning Models are particularly successful when applied to large volumes of complex data, such as images and voice recordings.
By using multiple layers of processing (referred to as hierarchical), Deep Learning Models can extract both low-level and high-level characteristics in data that would otherwise be undetectable with less sophisticated algorithms. The ability to create these complex models has led to significant advances across many areas of artificial intelligence, including autonomous vehicles and advanced natural language processing.
Neural Networks: The Backbone of Deep Learning
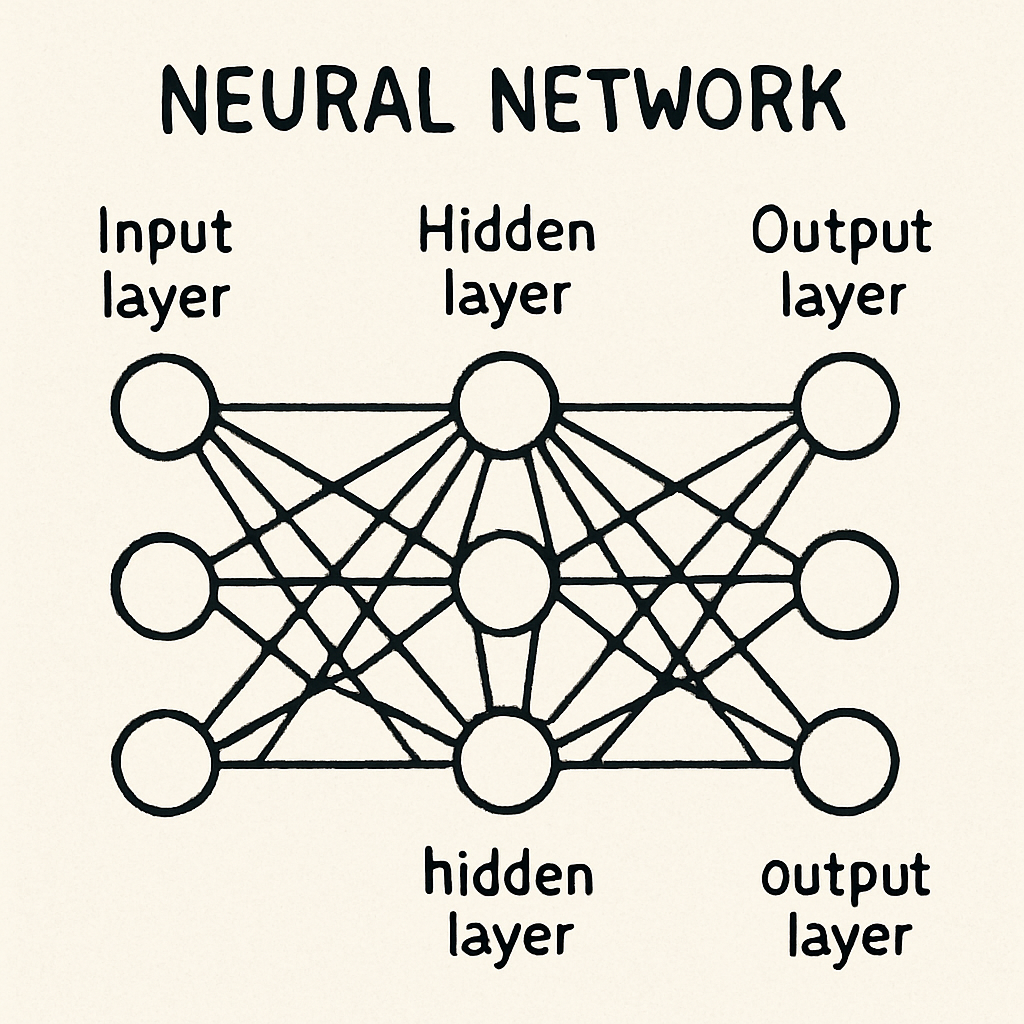
Deep Learning’s distinguishing characteristic is that it can automatically identify the necessary features to classify or predict an item from raw data (unlike other machine learning techniques, which require extracting these features manually). Neural Networks use Backpropagation to adjust their weights so they get closer to providing accurate classifications/predictions; thus allowing Deep Learning Models to achieve high levels of accuracy when working with unstructured data (images/audio), where a manual approach to feature engineering is either very difficult or outright impossible.
In a typical neural network architecture, there are multiple layers of nodes. The first layer of nodes receives data, the Input Layer, then passes through one or more Hidden Layers, and finally exits the last layer of nodes, the Output Layer. It is the connections between the different layers of nodes that enable the network to learn and build models of complex, nonlinear relationships in the data.
Key Differences Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
There are significant distinctions between deep learning and machine learning:
Data Dependency
Machine learning can perform well with small or medium-sized datasets. Machine learning is also very good at making an educated decision when you have a relatively limited amount of data, since most machine learning models are developed based on engineered features by a human. This reliance on feature engineering enables machine learning to excel when domain expertise is available to improve model performance, typically yielding more accurate outcomes across many applications.
Deep learning models need much more data than shallow models to function correctly, because deep learning is based on artificial neural networks; these networks require large amounts of data to “learn” and identify significant characteristics of a given body of information. The amount of data needed to train a deep learning model can significantly affect its performance.
Deep learning is, therefore, a good option when a lot of data is available for a particular problem, such as social media analysis or genomics, in which case there will be enough data to enable deep learning to succeed and produce very accurate answers.
Hardware Requirements
The high level of computational resources needed to develop Deep Learning Models is typically supplied through the use of specialized computer processors called Graphics Processing Units or “GPUs.” The reason GPUs can handle large volumes of data (which is necessary for developing Deep Learning Models) is the complexity of data flow within a neural network, including its numerous layers of interconnected nodes and the computations that occur at each layer.
Therefore, as Deep Learning Models involve an enormous number of mathematical calculations, the ability of GPUs to process data in parallel with other GPUs makes it the ideal processor for demanding applications of Deep Learning Algorithms. Because of their architecture, GPUs enable the simultaneous processing of datasets, resulting in shorter training times and improved application performance.
Unlike Deep Learning Algorithms, Machine Learning Algorithms are generally less computationally intensive in terms of hardware; as such, they typically function adequately with less capable hardware than Deep Learning Algorithms. Moreover, there is no requirement to use graphics processing units (GPUs) when implementing machine learning algorithms.
As a result, machine learning has become an increasingly viable and affordable alternative for organizations and researchers with limited or no access to high-powered computers. The relative ease of access to machine learning is the primary reason it is used in so many applications.
While machine learning does not require as much high-performance hardware as deep learning to train models rapidly and deploy them effectively, the hardware used to implement the machine learning algorithm will still affect the time and efficiency with which the model is trained and deployed. Thus, an adequate computational setup will also improve the overall performance of the machine learning model.
Feature Engineering
Feature Engineering is one of the most critical steps in the Machine Learning Process. During Feature Engineering, Domain Experts with deep domain and industry knowledge create or select Features that significantly improve the accuracy and performance of Machine Learning Models.
Therefore, the creation of appropriate Features requires sufficient domain knowledge and skills, as the selected Features must provide the Model with information to make accurate predictions. Because Feature Engineering is a manual process, it can be very time-consuming; however, by integrating domain knowledge and insights into the Model through Feature Engineering, the Model can produce better results.
Instead of relying on manual data manipulation through feature engineering, as many contemporary machine learning applications do, deep learning offers a novel approach that eliminates the need for such manipulation. Deep learning offers the advantage of automatically extracting relevant features from raw data, thereby simplifying model development.
Additionally, automatic feature generation is most beneficial in complex domains such as image and speech recognition (where it may require extensive domain-specific knowledge). The automation of feature learning provided by deep learning not only facilitates model development but also enables the exploration of entirely new possibilities and advances across many other areas involving unstructured data.
Execution Time
While there are many differences between machine learning and deep learning, a commonality is that models trained with both methods can be trained faster than their deep learning counterparts. The architecture of most deep learning models is complex and has a large number of parameters.
These complexities can lead to longer training times on the model due to increased computational requirements. Additionally, the iterative nature of the training process and the need to process all data before training begin increase the total time required to train the model.
Deep learning models, although often slower to train than machine learning models, can quickly process new data and generate predictions once trained. Deep learning’s faster processing times compared to machine learning,
for example, make it ideal for applications requiring real-time responses, such as analyzing live video feeds or navigating self-driving cars. Thus, in areas where decisions must be made rapidly and accurately, the rapid predictive capabilities of deep learning could confer an advantage. As such, practitioners should weigh the benefits of each (training speed vs. prediction speed) when deciding whether to use machine learning or deep learning methods.
Applications of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine Learning and Deep Learning are widely used across industries and sectors and have numerous applications, including in Finance.
Machine Learning Applications
Finance is an area in which machine learning is critical for Fraud Detection, Risk Management, and Stock Price Prediction. By using sophisticated machine learning models, organizations can analyze their customers’ or clients’ transaction history to identify irregularities that may indicate fraud. In addition, they can evaluate borrowers’ creditworthiness much more effectively than before and therefore make more informed lending decisions.
Finally, by analyzing large volumes of financial data, Machine Learning can provide valuable insights into market trends, enabling investors and companies to anticipate stock market changes and make strategic financial decisions.
Machine Learning has numerous applications in healthcare, including disease prediction and Personalized Treatment Plans. Machine Learning will enable Health Providers to analyze large volumes of patient data using advanced Algorithms, allowing them to predict future health problems before they occur and to intervene with the patient much earlier to improve overall health.
Additionally, Machine Learning will enable a Health Care Provider to identify the most appropriate course of treatment for an individual’s specific needs by analyzing those needs, ensuring the individual receives the most beneficial and appropriate method of care.
Machine Learning has been applied across multiple areas of Marketing, including Customer Segmentation, Recommendation Systems, and Sentiment Analysis. Machine Learning’s ability to analyze vast amounts of consumer data helps businesses identify trends, preferences, and behaviors in their target market, enabling more effective segmentation of their customer base.
Once segmented, companies can create targeted marketing efforts that are more likely to resonate with their customers. Machine Learning also enables the development of Recommendation Systems that suggest products to consumers based on their purchase history and product preference patterns, thereby increasing customer engagement. Finally, Machine Learning-based Sentiment Analysis Tools allow businesses to collect customer feedback and opinions, providing a better understanding of what their customers think and feel about their products and services.
Deep Learning Applications
Deep learning models have demonstrated excellent capabilities for analyzing and processing visual data. Therefore, they are beneficial for a wide variety of applications that require precise image/video analysis, such as autonomous vehicle navigation and object/individual detection. Facial recognition systems are another example of a deep learning application, in which models process images (photographs/videos) and identify faces and individuals within them.
Object detection models process video and image data to identify objects in a scene. These models also provide information about the size/location of each detected object.
NLP (Natural Language Processing) encompasses a range of tasks, including text-based sentiment analysis, chatbot development, and language translation. Deep learning has been a significant advancement in NLP, enabling computers to both understand and generate human language.
Advances in this new approach to language processing have enabled the development of more sophisticated and interactive applications that can engage users in conversation, provide real-time translations, and identify the emotional tone of written communication. Therefore, advancements in deep learning continue to enable us to develop ways for humans to use natural language to communicate with machines.
Deep Learning has enabled a wide range of Audio Recognition applications (e.g., Speech-to-Text, Virtual Assistants) by enabling the processing of large amounts of audio data.
It will be the ability of these advanced voice recognition systems to successfully interpret spoken language that will enable their success as a variety of Interactive Voice-Based Technologies. Using Deep Learning, developers can build applications that not only recognize and transcribe spoken language but also interact with Users in a more Natural way by responding to User Commands and Queries in Real Time, thereby enhancing the user experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between deep learning and machine learning is crucial when deciding which is best suited to your artificial intelligence project. Deep learning can deliver strong performance on small datasets or in scenarios where human experts are available to assist with tasks such as feature engineering. Due to its adaptability, deep learning offers a high degree of flexibility and ease of use, making it a viable and attractive option for many business applications, especially those with limited resources or constraints.
Deep Learning has many advantages over traditional machine learning, particularly its ability to efficiently and automatically extract features from enormous datasets. It enables the handling of much more complex tasks than previously possible (e.g., image and speech recognition), creating opportunities to develop state-of-the-art technology by leveraging deep learning’s exceptional capabilities for modeling high-level abstractions and processing unstructured data. Using the unique strengths of each machine learning type will enable you to create AI systems that are not only more efficient but also tailored to your project’s needs.
Having a good understanding of when to apply machine learning versus deep learning for many different types of projects (e.g., identifying fraud transactions; creating self-driving cars) will allow you to have better success with the kind of project you are working on.
To summarize, although machine learning and deep learning share commonalities, the two methods differ significantly, making them suitable for distinct use cases. As you begin your journey into AI, being aware of these differences is important because it will help you choose the appropriate tool(s) and methodology(ies) to achieve your objectives and overcome the challenges you may encounter.
Q&A
Question: What is the primary difference between machine learning and deep learning? Answer: The primary distinction between deep learning and machine learning is the way each method approaches data. Deep learning models use a type of artificial network called a multi-layered neural network (with many layers) to learn the characteristics of larger datasets automatically. Machine learning methods rely on manually engineered feature-based algorithms to train on features extracted from smaller data sets. This makes machine learning suitable for tasks like predictive modeling and classification. In contrast, deep learning is better suited to complex problems, such as image and speech recognition and natural language processing.
Question: How does supervised learning differ from unsupervised learning? Answer: Supervised Learning is when you give your Model Labeled Data, and it learns to match what’s in the Input with what’s in the Output. Unsupervised Learning is when you give your Model Raw Data (no labels), and it learns to find Patterns or Groupings on its own. That means that the Model doesn’t know anything about the Outcome.
Question: When do I use machine learning instead of deep learning? Answer: You will want to use machine learning in cases where you have a limited number of samples, or if you have domain knowledge about your data that allows you to create meaningful features through feature engineering. In addition, you would want to use machine learning when interpretability (you need to understand how your model works), training speed, and minimal computing resources are key to your project.
Question: What are some typical applications of deep learning? Answer: Deep Learning has many application areas. Some examples include Computer Vision (e.g., facial recognition, object detection), Natural Language Processing (e.g., language translation, chatbots), and Audio Recognition (e.g., voice commands, speech-to-text).
Question: What role does data volume play in the effectiveness of machine learning and deep learning? Answer: Data Volume plays a critical role in Machine Learning & Deep Learning success. Machine Learning can be successful with smaller or medium-sized datasets and manual feature selection. However, Deep Learning is most successful when large amounts of data exist. It enables the automatic extraction of feature sets that may have been difficult or time-consuming to identify, and it supports the learning of complex patterns in the data; this will lead to better results as more data are input into the system.